A DC gear motor combines a DC motor with a gearbox, providing controlled rotational force. These essential components are found in countless applications, from industrial automation to smart home devices. The global miniature DC geared motor market, valued at approximately $11.4 billion in 2024, projects robust growth to $19.28 billion by 2032, underscoring their widespread importance. Selecting the right motor is critical for optimal system operation and longevity; a mismatch in torque and speed can lead to failures and increased costs. The core challenge involves balancing torque, speed, and gear ratio to meet specific application demands. This guide provides a comprehensive methodology for confident motor selection, helping you choose the best DC gear motor for high performance.
Key Takeaways
A DC gearmotor combines a DC motor with a gearbox. This gives controlled power for many uses.
You must balance torque, speed, and gear ratio. This helps you choose the right gearmotor for your needs.
Gearboxes increase torque and reduce speed. This makes the motor more useful for different jobs.
Always define your application’s needs first. Then, calculate the required torque and speed.
The gear ratio balances motor speed with the load’s torque needs. A higher ratio means more torque but less speed.
Consider more than just torque and speed. Look at electrical needs, size, environment, and efficiency.
Avoid common mistakes like ignoring load needs or environmental factors. Do not choose cheap over quality.
Test your chosen gearmotor well. This ensures it works correctly in real-world conditions.
DC Gearmotor Fundamentals
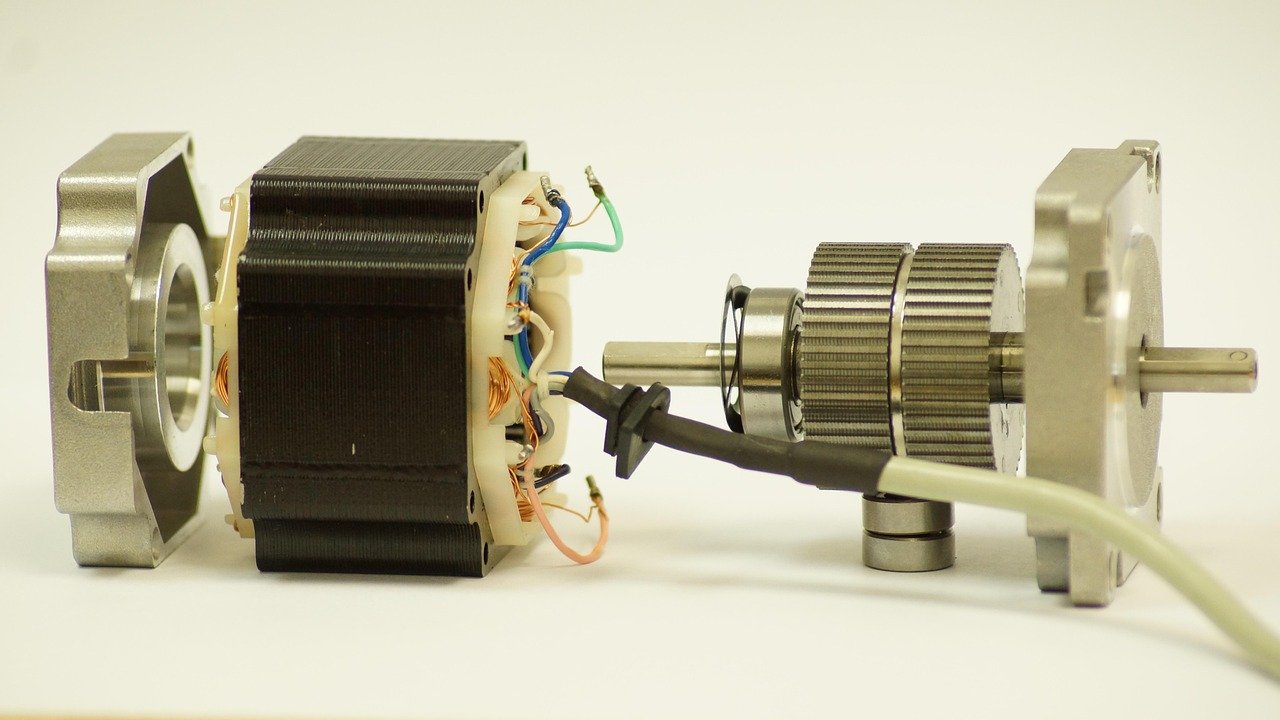
Understanding DC gearmotor basics helps you make informed choices. A DC gear motor combines a DC motor with a gearbox. This combination creates a powerful and versatile unit.
DC Gear Motor Overview
Motor Component Basics
The motor is the heart of any DC gear motor. It generates rotational motion. Typically, you will find either a brushed or brushless DC motor. These motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Gearbox Component Basics
The gearbox is a system of gears. It modifies the motor’s output torque and speed. This system allows the DC gear motor to achieve specific operational characteristics.
Key Performance Parameters
You need to understand several key performance parameters for proper selection.
Torque: Rotational Force
Torque is the rotational force a motor produces. You measure torque in units like Newton-meters (Nm) or ounce-inches (oz-in). A higher torque means the motor can turn heavier loads.
Speed: RPM Explained
Speed refers to how fast the motor shaft rotates. You measure speed in revolutions per minute (RPM). This parameter tells you the motor speed.
Power: The Work Metric
Power is the rate at which a motor does work. You calculate power from torque and speed. It indicates the overall capability of the motor.
Gear Ratio: Mechanical Advantage
The gear ratio is a critical parameter. It describes the relationship between the number of teeth on two interacting gears. For example, a 1:3 ratio means the driven gear completes one-third of a rotation for every rotation of the driving gear.
The gear ratio dictates the system’s output speed and torque:
A higher gear ratio (e.g., 100:1) increases torque output while reducing the output speed, providing mechanical advantage.
A lower gear ratio (e.g., 2:1) increases speed but reduces the available torque.
Understanding gear ratios in DC gear motors is essential for achieving the required mechanical advantage and optimizing system performance.
Why Gearboxes are Essential
Gearboxes are vital components in DC gear motors. They Modulate speed and torque, making the gearmotor more versatile.
Torque Multiplication
Gearboxes excel at torque multiplication. They increase the output torque from the DC motor. This is crucial for applications needing significant force, like lifting or drilling.
Speed Reduction
Gearboxes also provide speed reduction. They reduce the motor’s output speed to a usable level. This allows for precise control and prevents over-speeding.
Inertia Matching Principles
Gearboxes help match the motor’s inertia to the load’s inertia. This improves system stability and efficiency. Optimizing gear ratios enhances mechanical advantage. This contributes to energy efficiency by matching the motor’s characteristics with application requirements.
Your DC Gearmotor Selection Guide: The Process
You need a systematic approach for selecting a DC gear motor. This guide walks you through each step. It helps you define requirements and verify power. This process ensures you make the best selection for your application.
Define Application Requirements
First, you must clearly define your application’s needs. This initial step is crucial for effective DC gearmotor selection. You cannot choose the right gearmotor without understanding what it needs to do.
Identify Load Type
You must identify the type of load your gearmotor will handle. Different loads demand different motor characteristics. Classifying the load by application helps quickly determine the primary performance requirements:
Precision Automation & Robotics: Requires high torque, excellent positional accuracy, and minimal backlash (e.g., collaborative robots, high-speed pick-and-place systems, robotic arms).
Heavy Industrial & Material Handling: Demands high starting and running torque, continuous duty operation, and high durability (e.g., cranes, hoists, conveyor belt systems, packaging machinery).
Automotive & RV Systems: Needs controlled, reliable motion, and high temperature/vibration resistance (e.g., window lifts, seat adjusters, RV slide-out mechanisms).
Medical & Home Automation: Focuses on ultra-quiet operation, high energy efficiency, and precise control in a compact design (e.g., precision surgical tools, smart locks, automatic curtains).
By classifying the application type, you establish the foundational requirements for torque, speed, and environmental suitability, which guides the subsequent calculation steps.
Determine Output Motion
Next, determine the exact output motion you need. Will the gearmotor rotate continuously, or will it move in specific increments? Do you need linear motion, or is rotational motion sufficient? Understanding the desired motion helps you narrow down your choices.
Specify Operating Cycle
You must specify the operating cycle. Will the gearmotor run continuously, or will it operate intermittently? Continuous duty cycles require motors designed for sustained operation without overheating. Intermittent cycles might allow for smaller, less expensive motors.
Calculate Load Torque & Speed
After defining your application requirements, you calculate the necessary load torque and speed. This step involves some fundamental physics.
Estimate Static Torque
Static torque is the rotational force needed to hold a load stationary or to overcome non-moving friction. You calculate torque (T) by multiplying the force (F) by the radius (r) from the center of rotation (T = F x r). This fundamental formula helps you find the turning force required. For example, if a robotic arm applies 30 Newtons of force at a radius of 0.5 meters, the torque is 15 Nm. Static loads remain constant, like holding an object still or counteracting gravity. Although static loads require zero power, the motor you select must have a sufficient rated torque to overcome this static resistance, and its power (P) will be determined by the speed (N) at which it needs to move the load, following the relationship: P = M * N / 9550η (where M is torque and η is efficiency).
Calculate Dynamic Torque
To manage dynamic loads effectively, engineers focus on Inertia Matching. This involves balancing the load inertia (J_L) with the motor’s inertia (J_M) to ensure stable, precise control and minimized wear. While precise calculation involves complex formulas, the engineering principle is simple: the ratio of load inertia to motor inertia (J_L / J_M) should ideally fall within an industry-recognized range (e.g., 1:1 to 10:1). Adhering to this principle is crucial for optimizing system responsiveness and maximizing the lifespan of the gearmotor.
Establish Output Speed
You must establish the required output speed. This is the speed at which your application needs to operate. You measure it in RPM. This value directly influences your gear ratio selection.
Selecting the Gear Ratio
Choosing the right gear ratio is a critical step in DC gearmotor selection. It balances the motor’s inherent speed with the application’s torque demands.
Calculate Ideal Gear Ratio
You can calculate the ideal gear ratio by dividing the input speed (motor RPM) by the desired output speed. For applications where torque is critical, you determine the ratio by dividing the load torque by the available motor torque. Always include appropriate safety factors. For multi-stage gearboxes, you find the total gear reduction by multiplying the individual ratios of each stage. The ideal gear ratio is always chosen based on the specific requirements of the application. Avoid common errors like confusing input and output gears or overlooking that idler gears do not influence the overall ratio.
Application Type | Typical Gear Ratio | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Conveyor Systems | 20:1 to 50:1 | High torque for heavy loads |
Drilling Equipment | 100:1 to 500:1 | Maximum torque multiplication |
Pump Drives | 2:1 to 10:1 | Balanced speed and torque |
Mixers/Agitators | 10:1 to 30:1 | Controlled mixing speed |
Gear Ratio Trade-offs
A higher gear ratio increases torque output but reduces speed. A lower gear ratio increases speed but reduces torque. You must balance these trade-offs to meet your application’s specific needs. This balance is key to optimal gearmotor performance.
Standard Gear Ratios
N20 DC motor gearmotors are available with a wide range of gear ratios. These include ratios like 1:5 to 1:1000, 1:3 to 1:750, and specific examples like 1:120. An N20 DC motor provides higher torque at lower speeds due to its integrated gearbox. This contrasts with regular DC motors that run faster but struggle with heavy loads. Customization options, including gear ratios, allow you to balance speed and torque for specific application needs. The output speed of N20 DC motor gearmotors varies significantly depending on the gear ratio. Examples range from 20 rpm to 2000 rpm, 54 rpm, and 12 rpm to 1500 rpm.
Verify Motor Power & Torque
You have defined your application needs and calculated the required load torque and speed. Now, you must verify that your chosen motor can meet these demands. This step is crucial in your DC gearmotor selection guide. It ensures your system performs reliably.
Required Motor Input Torque
First, calculate the motor’s required input torque. You do this by dividing the load torque by the chosen gear ratio. Remember to factor in the gearbox’s efficiency. A gearbox always has some losses. For example, if your application needs 10 Nm of torque and your gear ratio is 50:1, the motor needs to produce at least 0.2 Nm of torque before losses. This calculation helps you find a DC motor with enough raw power. You need to ensure the motor can deliver the necessary torque output at the required speed.
Ensure Power Meets Demands
Next, confirm the motor’s power rating is sufficient. You can calculate the required power from the desired output torque and speed. The motor’s rated power must be greater than your calculated requirement. This ensures the motor can handle the load without overworking. A motor operating near its maximum limits will wear out faster. It might also fail to deliver consistent torque output. Always choose a gearmotor with a bit of extra power. This provides a safety margin.
Account for Efficiency Losses
Not all the power a DC motor generates reaches the output shaft. Energy losses occur throughout the system. You must account for these losses to make an accurate selection.
Gearbox Losses:
Friction: Moving parts rub against each other. This happens in gears, bearings, and shafts. This friction creates lost energy.
Pocketing and Churning: Gears push oil and air as they turn. This action causes energy loss.
Windage: Fast-spinning gears push against air or oil. These losses increase with speed and oil temperature. Oil and air pressure contribute significantly, especially at higher speeds.
Friction between teeth: This is a direct source of energy loss.
Backlash: Misaligned gears waste energy.
Material properties: Steel gears create more friction than materials like nylon. This impacts efficiency. These issues can lead to a 5% to 20% efficiency loss in a DC gear motor.
Motor Losses:
Heat from wires: Electrical current flowing through wires generates heat. This represents lost energy.
Magnet losses: Inefficiencies relate to the motor’s magnets.
Internal friction: Friction occurs within the motor’s electrical components.
Some electrical energy converts into heat. This heat can damage the DC motor.
You should keep the safe case temperature below 90°C. This prevents bearing grease breakdown and extends motor lifespan.
High loads, inadequate cooling, frequent starts and stops, and high ambient temperatures cause overheating.
Even small temperature increases lead to higher current draw. This creates more heat and accelerates wear.
For a small DC gear motor, like an n20 DC motor, these losses can be significant. They impact the final available torque and speed. Always choose a motor with a higher rated power than your calculated need. This compensates for these unavoidable efficiency losses.
Beyond Torque & Speed: Key Considerations for DC Gear Motors

You must look beyond just torque and speed when choosing a DC gear motor. Other factors significantly impact your system’s performance and longevity. These include electrical, physical, and environmental aspects.
Electrical Specifications
You need to understand the electrical needs of your gearmotor. This ensures compatibility with your power source and control system.
Voltage Requirements
Your application’s voltage determines the motor you select. Most low-voltage DC gear motors operate between 1.5V and 24V. For example, robots often use motors running on 6V, 12V, or 24V. You must match the motor’s rated voltage to your power supply.
Motor Type | Rated Voltage (VDC) | No Load Current (mA) |
|---|---|---|
N20 Brushed DC | 1.5 to 12 | ~50-60 |
3V Brushed DC | 2.5 to 12 | ~60 |
Planetary Gear | 1.5 to 12 | ~50 |
General DC Gear | 1.5 to 24 | Tens to hundreds |
Current Draw & Power Supply
Motors draw current to produce torque. A motor draws more current when it delivers higher output torque. The stall current, when the motor is stopped, represents the maximum current draw and maximum torque. Low voltage dc motors (e.g., 12V or lower) can draw from 100mA to several amperes when stalling. Starting current can be up to eight times higher than running current. Your power supply must handle these surges, especially for low-voltage motors. A good power supply ensures stable motor operation.
Brushed vs. Brushless DC Solutions
You have two main types of DC motors: brushed and brushless. Each offers distinct advantages.
Brushed DC Motors: These motors are cost-effective and offer high starting torque. They provide simple speed control.
Brushless DC Motors: These motors offer high efficiency, longer lifespan, and precise speed control. They are often more expensive but require less maintenance.
Honest Motor offers brushed DC motors with power ratings from 90-300W, operating at 18-310V, and speeds from 3000-7000 RPM. You can customize brush materials, coil design, and torque curves within DC 5V-400V, power 3W-5000W.
Physical Size & Mounting
The physical characteristics of your gearmotor are just as important as its electrical ones.
Space Constraints
You must consider the available space in your application. A DC gear motor needs to fit physically. Measure the dimensions carefully.
Mounting Configuration
How you mount the gearmotor affects its stability and integration. Common mounting options include face-mount, flange-mount, and base-mount. Choose a configuration that securely holds the gearmotor in place.
Shaft Type & Connection
The motor’s shaft connects to your load. DC gearmotors typically range from 4mm to over 42mm in diameter. Shaft configurations include standard round, D-shaped, and threaded shafts. For 12V dc gear motors with high torque gearboxes, shaft sizes commonly range from 3 mm to 8 mm. Larger shafts may be necessary for heavy-duty applications to handle higher torque.
Environmental Factors
The operating environment significantly impacts gearmotor performance and lifespan.
Operating Temperature
Extreme temperatures can degrade motor components. High temperatures reduce motor efficiency and shorten its life. Low temperatures can affect lubrication and material properties. Honest Motor offers extreme customization for harsh environments, including high and low-temperature applications.
Ingress Protection (IP) Ratings
IP ratings tell you how well a gearmotor protects against solids and liquids. The IEC developed the IP system in 1976. It provides a standardized rating for electric motors. This system classifies protection against water, dust, and other solid objects. Each IP code has two numbers. The first digit shows protection against solid objects. The second digit shows protection against water. For example, an IP54 rating means the motor is dustproof and protects against water splashed from all directions.
Digit | Protection Against Liquids | |
|---|---|---|
0 | No protection | No protection |
1 | Protection against solid objects > 50 mm | Protection against vertically falling water drops |
2 | Protection against solid objects > 12.5 mm | Protection against vertically falling water drops (enclosure tilted up to 15 degrees) |
3 | Protection against solid objects > 2.5 mm | Protection against water sprayed at an angle of up to 60 degrees |
4 | Protection against solid objects > 1 mm | Protection against water splashed from any direction |
5 | Protection against dust (limited ingress, no harmful deposits) | Protection against water jets from any direction |
6 | Complete protection against dust (no ingress) | Protection against powerful water jets and heavy seas |
7 | Complete protection against dust (no ingress) | Protection against immersion in water up to 1 meter for 30 minutes |
8 | Complete protection against dust (no ingress) | Protection against continuous immersion in water under manufacturer-specified conditions |
9 | Complete protection against dust (no ingress) | Protection against high-pressure, high-temperature water jets |
Vibration & Shock Resistance
Applications with high vibration or shock require robust gearmotors. These motors need strong construction and secure components. This prevents damage and ensures reliable operation.
Efficiency, Noise, & Backlash
You must also consider gearbox efficiency. This tells you how much power the gearbox loses. Gearboxes do not transfer 100% of the motor’s power. Some energy always turns into heat or friction. This affects the final output torque and speed. For example, spur, helical, and double helical gearboxes are very efficient. They typically operate at 98-99% efficiency. Bevel gearboxes also show high efficiency, around 98-99%. However, worm gearboxes can have a wider range, from 20-98% efficiency. Crossed helical gearboxes might range from 70-98%. Industrial gearboxes usually achieve 95% to 98% efficiency. Automotive gearboxes are often between 90% and 95%. Wind turbine gearboxes aim for 96% to 98%. Marine gearboxes commonly show 94% to 97% efficiency. You want to optimize efficiency to ensure your DC gear motor performs well.
Gearbox Efficiency
Different gearbox designs offer varying levels of efficiency, which directly impacts the final output power and energy consumption.
Refer to the table below for common efficiency ranges:
Efficiency Range | |
|---|---|
Spur | 98-99% |
Helical | 98-99% |
Double Helical | 98-99% |
Bevel | 98-99% |
Worm | 20-98% |
Crossed Helical | 70-98% |
Noise Level Considerations
Noise is another important factor. Some applications need quiet operation. Think about smart home devices or medical equipment. A noisy gearmotor can be a problem. You should look for gearmotors designed for low noise. This often means precision manufacturing and good lubrication. High speed operation can sometimes increase noise.
Minimizing Backlash for Precision
Backlash is the small amount of play between gear teeth. It is like a tiny gap. This gap can reduce precision. It affects how accurately you can control output torque and position. For applications needing exact positioning, you must minimize backlash. High-quality, precision gearmotors often offer ultra-low backlash, with specifications frequently reaching ≤ 5 arc minutes , a crucial requirement for robotic joints and precision equipment. You can achieve precision by using several methods:
Precision Gears: Manufacturing with tighter tolerances results in a more precise fit. This means less play between gear teeth.
Shortening Center Distance: Reducing the distance between gears ensures teeth mesh more tightly.
Pre-loading Mechanisms: Utilizing spring mechanisms holds gears firmly in place. This eliminates play.
Specific Gear Types: Employing gears like strain wave gears inherently offers zero backlash.
A mechanical anti-backlash gear also helps. It uses two cog wheels on the motor side. A stiff spring connects them. This spring keeps the backlash gap closed. However, this method can sometimes add resonance. This might limit how fast your control system can respond.
Control System Compatibility
You need to ensure your gearmotor works with your control system. This means checking how you connect and manage the motor.
Motor Driver Integration
A motor driver controls your gearmotor. It takes signals from your main controller. Then, it sends power to the dc gear motors. You must choose a driver compatible with your DC gear motor’s voltage and current. The driver also needs to support the type of DC motor you have.
Feedback Options
Feedback helps your control system know what the gearmotor is doing. This is crucial for accurate speed and position control. Encoders are common feedback devices. They tell you the motor’s speed and position.
Absolute Encoder: This tracks full or many turns. You use it in assembly lines and long-travel systems.
Incremental Encoder: This sends pulses for speed and direction. You find it in robotic arms, packaging, and electric vehicles.
Magnetic Encoder: This uses magnets. It works well in tough places like automotive and industrial DC motors.
Optical Encoder: This is very accurate. It uses light sensors. You see it in CNC machines, 3D printers, and medical imaging.
Capacitive Encoder: This senses motion. It uses little power. You find it in portable devices.
Single Turn Encoder: This measures one full turn. It is useful for robotic joints and servo motors.
Multi-Turn Encoder: This tracks many turns for long moves. You use it in industrial robots and big conveyors.
Hall sensors are also common. They are often built into brushless dc motors. They help with commutation. Their outputs can also give speed feedback. This works for applications needing lower resolution. Examples include pizza ovens or remote pumps. You can access this signal through the speed control. This means you do not need a separate encoder. Some gearmotors offer specific designs for encoders. An accessory shaft provides an external extension. This allows mounting modular, hollow-bore encoders. A shaft extender has a hole in the motor endshield. You can add an extender for encoder mounting. This keeps the high-speed shaft covered if you do not need an encoder.
Types of DC Gear Motors & Their Applications
You find many types of gearboxes in DC gear motors. Each type offers unique benefits for different applications. Understanding these differences helps you choose the best gearmotor.
Gearbox Types Compared
You can compare gearboxes based on their design and performance.
Spur Gearboxes
Spur gearboxes are simple and reliable. They are inexpensive to produce. You use them in light-duty applications like packaging and food processing. They offer minimal power transmission losses. However, they can be noisy during operation.
Planetary Gearboxes
Planetary gearboxes are compact. They offer high power density. You use them for precise speed and torque control. Robotics and printing presses often use them. They are more complex and expensive, requiring higher maintenance.
Worm Gearboxes
Worm gearboxes are also compact. They provide high torque output. You find them in heavy-duty applications like cranes and hoists. They can be less efficient, generating more heat and noise. This can reduce their service life.
Helical Gearboxes
Helical gearboxes operate smoothly and quietly. They are highly efficient. You choose them when noise or energy consumption is a concern. They have higher manufacturing costs and specific maintenance needs. They offer greater load-carrying capacity and improved torque transmission.
Characteristics | Ventajas | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|---|
Planetary | Compact design, high power density; ideal for precise speed and torque control in robotics and printing presses. | High power density, compact design, precise speed and torque control. | Relatively expensive, complex design, higher maintenance costs. |
Worm | Compact design, high torque output; used in heavy-duty applications like cranes and hoists. | Compact design, high torque output. | Inefficient, heat and noise generation, reduced service life. |
Helical | Smooth and quiet operation, high efficiency; ideal for applications where noise or energy consumption is a concern. | Smooth and quiet operation, high efficiency. | Higher costs, maintenance requirements. |
Spur | Reliable and inexpensive; used in light-duty applications such as packaging and food processing. | High reliability, inexpensive, minimal losses in power transmission. | Noisy operation, reduced service life. |
Real-World Applications
DC gear motors power many devices you use every day. They provide controlled motion across various industries. These common uses for DC gearmotors highlight their versatility.
Industrial Automation & Manufacturing
Industrial automation solutions prioritize precision control, energy efficiency, and durability.
Mobile Robot Drive Systems: Small DC gear motors power wheels or tracks for precise movement in warehouse robots.
Automated Conveyor Systems: They move belts for material handling on assembly lines.
Robotic Arms: These motors provide controlled and accurate movement. They allow arms to lift heavy objects without shaking.
Valve Control: Gearmotor solutions offer secure actuation for systems, often requiring explosion-proof and corrosion-resistant features for compliance in hazardous environments.
Household & Commercial Appliances
Motors for appliances focus on energy efficiency, ultra-low noise, and longevity.
Food Processing: Motors power equipment like meat grinders and dough mixers.
Beverage Preparation: Precision motors are used in coffee grinders.
HVAC: Motors provide reliable power for air conditioners.
Gaming Chairs: They offer precise haptic feedback and quiet operation.
Automatic Curtains: These motors provide smooth, quiet operation for smart homes.
Electronic Door Locks: They ensure secure and reliable locking mechanisms.
Oil & Gas Industry
This sector requires extremely robust motors that can operate reliably in harsh, often corrosive, atmospheres and under intense vibration.
Downhole and Directional Drilling: Brushless DC motors control hydraulic valves and communication mechanisms.
Mud Pumps: DC motors function as generators using mud flow in drilling operations.
Fluid Control: DC actuators regulate gases, liquids, and crude petroleum.
Oil Skimmers: Custom DC gear motor designs are built for these specialized tools. These motors withstand intense vibration and corrosive atmospheres. They provide the necessary torque and speed for critical operations.
For developers seeking customized, high-reliability DC gear motor solutions covering all the specialized sectors listed above, reputable manufacturers like Honest Motor offer advanced design and production capabilities to meet these specific industry demands.
Quality, Reliability, and Cost in DC Gearmotor Selection
You must consider quality, reliability, and cost when choosing a DC gear motor. These factors ensure your system’s long-term success.
Ensuring Quality & Compliance
Quality assurance starts with adherence to industry standards.
Industry Certifications
Key certifications include ISO 9001, IATF16949, CE, UL, RoHS, and REACH. Ensure the chosen gearmotor and its manufacturer comply with these standards. This confirms product quality and safety, ensuring you receive a reliable and safe product.
Rigorous Testing
Every motor undergoes 100% inspection of key processes and performance. This includes noise tests, on-load tests, and rotor performance checks. High-quality manufacturers conduct rigorous electrical, mechanical, and performance tests on every DC motor before shipment.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Consider the total cost of ownership, not just the initial price.
Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Value
Buyers prioritize long-term value. This includes energy efficiency and durability. Higher-quality gearmotors often cost more initially. However, they lead to a reduced total cost of ownership (TCO). This is due to their longer lifespans and better performance. A car wash business, for example, saw significant savings by switching to a more expensive, energy-efficient DC motor. The savings quickly recouped the initial investment.
Energy Efficiency & Operating Costs
Energy efficiency directly impacts operating costs. DC motors are generally more energy-efficient than their AC counterparts, converting more electrical energy into mechanical energy and reducing wasted power.
High-efficiency synchronous motors can achieve ultra-premium standards (equivalent to IE5 or IE6 levels), and specialized DC motors can reach efficiencies exceeding 93%. This high efficiency leads to lower utility bills and an extended motor lifespan due to reduced heat generation.
Maintenance & Lifespan
DC motors typically have fewer moving parts. This results in easier maintenance and a longer lifespan. Evaluating TCO, which includes maintenance and energy savings, is a key recommendation for your selection.
A significant component of an electric motor’s lifetime cost is its energy consumption. This accounts for 96% of the total. This underscores the critical importance of overall efficiency over the initial purchase cost. Investing in ultra-high efficiency synchronous motors (meeting or exceeding IE5 standards) can lead to rapid payback periods, often less than one year. The adoption of such premium standards often results in a significant reduction in energy losses compared to commonly used IE3 motors. This substantially lowers the Total Cost of Ownership, with the resulting energy savings frequently leading to a payback time of less than one year.
After-Sales Support & Warranty
Good support ensures peace of mind and continuous operation. When selecting a partner, look closely at their commitment to service after the sale.
Comprehensive Warranty
A strong warranty protects your investment. Standard warranty periods typically range from 1 to 3 years. Premium manufacturers often stand behind their product by offering guarantees at the high end of this range, including clear policies for repair, replacement, or refund for defects.
Responsive Technical Support
You need accessible and responsive support. Reputable manufacturers should offer guaranteed, rapid engineer response times for online support, often within 12 to 24 hours. They should also provide comprehensive maintenance guidance and technical assistance throughout the product’s lifespan.
Global Logistics & Supply Chain
Consider the manufacturer’s logistics capabilities. Look for partners with a robust global delivery network and those who partner with international freight forwarders. This ensures efficient and traceable logistics. Inquire about their manufacturing footprint, minimum order quantity (MOQ), and standard lead times. Reliable suppliers should offer competitive lead times (typically 3–4 weeks for bulk orders) and quick sample availability.
Common Mistakes in DC Gearmotor Selection
Overlooking Load Requirements
You often make mistakes by not fully understanding your load requirements. Misinterpreting torque-speed data can lead to inadequate starting torque. This results in poor performance or complete motor failure. Ignoring load changes and operating conditions also causes problems. Frequent starts, sudden load changes, or harsh environments like heat, humidity, or vibration can cause extra wear. This shortens the motor’s lifespan. Running a motor outside its optimal efficiency zone wastes energy. It also generates excessive heat. This lowers overall efficiency and reduces the motor’s lifespan. Operating a dc motor or gearmotor at its physical stall conditions can lead to significantly faster degradation. It can even cause instant failure. Prolonged operation near or at maximum torque limits puts substantial strain on the gear train. This causes the gearbox to fail much sooner than you expect.
Ignoring Environmental Factors
You must consider the environment where your gearmotor will operate. Ignoring the operating environment during dc gearmotor selection can lead to reduced durability of the motor. Extreme heat or cold can reduce motor efficiency or cause complete failure. High humidity can lead to rust and electrical problems. This significantly shortens the motor’s lifespan. Studies indicate that temperature fluctuations can significantly impact performance. Lab tests showed 91.4% of results were affected by temperature. Operating a DC gearmotor above its maximum rated temperature can lead to demagnetization of permanent magnets. It can also cause breakdown of winding insulation. This results in permanent motor failure. The motor generates its own internal heat. This heat adds to the ambient temperature. You need a DC motor with a higher temperature rating or greater efficiency in hot environments.
Prioritizing Low Cost Over Quality
You might feel tempted to choose the cheapest gearmotor. However, prioritizing low cost over quality often leads to higher long-term expenses. A low-cost gearmotor may use inferior materials. It might also have less precise manufacturing. This can result in frequent breakdowns and costly repairs. You will spend more money on maintenance and replacements. A higher quality gearmotor offers better reliability and a longer lifespan. It performs consistently and reduces downtime. Investing in a durable gearmotor saves you money over time. It ensures your system operates smoothly and efficiently.
Neglecting Maintenance & Lifespan
You often overlook the importance of regular maintenance for your DC gearmotor. This oversight significantly shortens its operational lifespan. Every DC motor, especially one paired with a gearbox, experiences wear and tear. Components like bearings, gears, and brushes (in brushed dc motors) degrade over time. Ignoring these signs of wear leads to increased friction and reduced efficiency. You might notice your DC gearmotor becoming noisier or running hotter. These are clear indicators of impending failure.
Proactive maintenance involves routine inspections, lubrication, and timely replacement of worn parts. When you neglect these simple steps, you invite unexpected breakdowns. These failures cause costly downtime and require expensive emergency repairs or full replacements. A well-maintained dc gearmotor operates reliably for its intended lifespan, sometimes even longer. You save money in the long run by investing a little time in its care. Remember, a small investment in maintenance prevents much larger expenses later.
Inadequate Testing & Verification
You cannot simply install a DC gearmotor and expect it to perform perfectly. Inadequate testing and verification represent a critical mistake in the selection process. You must thoroughly test your chosen DC gearmotor under real-world conditions. This includes simulating maximum load, varying speeds, and environmental extremes. Testing validates whether the DC gearmotor meets all your application’s specific requirements.
Prototype testing allows you to identify potential issues early. You can catch problems like overheating, insufficient torque, or excessive noise before mass production. This early detection saves significant costs and avoids redesigns. You should also perform endurance tests to confirm the dc gearmotor’s expected lifespan. Verify that the DC motor maintains its performance over extended periods. Comprehensive testing ensures your final product is reliable and performs as expected. It confirms the suitability of your initial DC gearmotor selection.
Successful DC gearmotor selection is a critical engineering task. It demands a thorough understanding of your application needs and a systematic motor selection approach. You must match key motor parameters like torque and speed. This DC gearmotor selection guide helps you balance torque, speed, and gear ratio with other practical factors for optimal performance. Always consider load, environment, and electrical specifications. Apply this knowledge to confidently choose the best DC gearmotor for your projects.
For projects demanding the highest levels of customization, ultra-low backlash, and compliance with standards for harsh environments, reputable manufacturers like Honest Motor offer the advanced engineering and reliable global support necessary to meet these mission-critical demands.
Take the final step in selection: Contact our engineering team today to discuss your project’s specific needs.
FAQ
What is the main purpose of a DC gearmotor?
A DC gearmotor combines a DC motor with a gearbox. It provides controlled rotational force. You use it to increase torque and reduce speed. This makes it suitable for many applications needing precise motion.
Why do gearboxes matter in DC gearmotors?
Gearboxes are essential. They multiply the motor’s torque. They also reduce its speed. This allows the gearmotor to handle heavier loads. It also provides more precise control for your application.
How do you calculate the ideal gear ratio?
You calculate the ideal gear ratio by dividing the input speed by the desired output speed. For torque-critical tasks, divide the load torque by the available motor torque. Always include safety factors in your calculation.
What is the difference between brushed and brushless DC motors?
Brushed DC motors are cost-effective and offer high starting torque. Brushless DC motors provide higher efficiency and a longer lifespan. They also require less maintenance for your system.
What does an IP rating mean for a gearmotor?
An IP rating tells you how well a gearmotor protects against solids and liquids. The first digit shows solid object protection. The second digit shows water protection. For example, IP65 means dust-tight and protected from water jets.
Why is minimizing backlash important?
Backlash is the small play between gear teeth. Minimizing it improves precision. This ensures accurate control of output torque and position. You need low backlash for exact positioning in your applications.